Innovative cancer therapy
Curing cancers without surgery
Proton Therapy not only cures cancer without excision, but also cures cancer that cannot be removed.
This radiation therapy irradiates cancer lesion with a pinpoint accuracy while minimizing the effect on surrounding normal cells. It is a gentle medical treatment that patients could choose without having to go through the excision surgery. Cancer is now becoming to be a disease that could be cured without resection. There are countless reasons why people are unable to take surgery, have limited treatment options, or want to avoid surgery or hospitalization. We are working on the proton therapy with a hope to be a ray of light for such patients.
The proton beam stops exactly at the depth of the tumor.
The effect on surrounding normal tissue is minimized.
Differences between Proton Therapy and x-ray therapy
Radiation used in cancer treatment can be divided into two main categories: photon beams and particle beams. X-rays used in conventional radiation therapy are photon beams, and proton beams are a type of particle beam.
In Proton Therapy, protons, the atomic nucleus of hydrogen, are accelerated to nearly 60% of the speed of light and hit the cancer cells, killing them. All cells have double helix DNA (genes) that control cell division. Proton beams have the destructive power to cut both strands of a cancer cell’s DNA, preventing it from growing.
In addition, proton beams have the physical property of creating a peak of energy (Bragg peak) at a certain depth and releasing all of their energy just before stopping. Another feature of Proton Therapy is that it can target cancer accurately while minimizing the impact on organs and surrounding normal cells near the cancer. Because no scalpel is inserted into the body and side effects are minimized, treatment can be done outpatient, depending on the type of cancer.
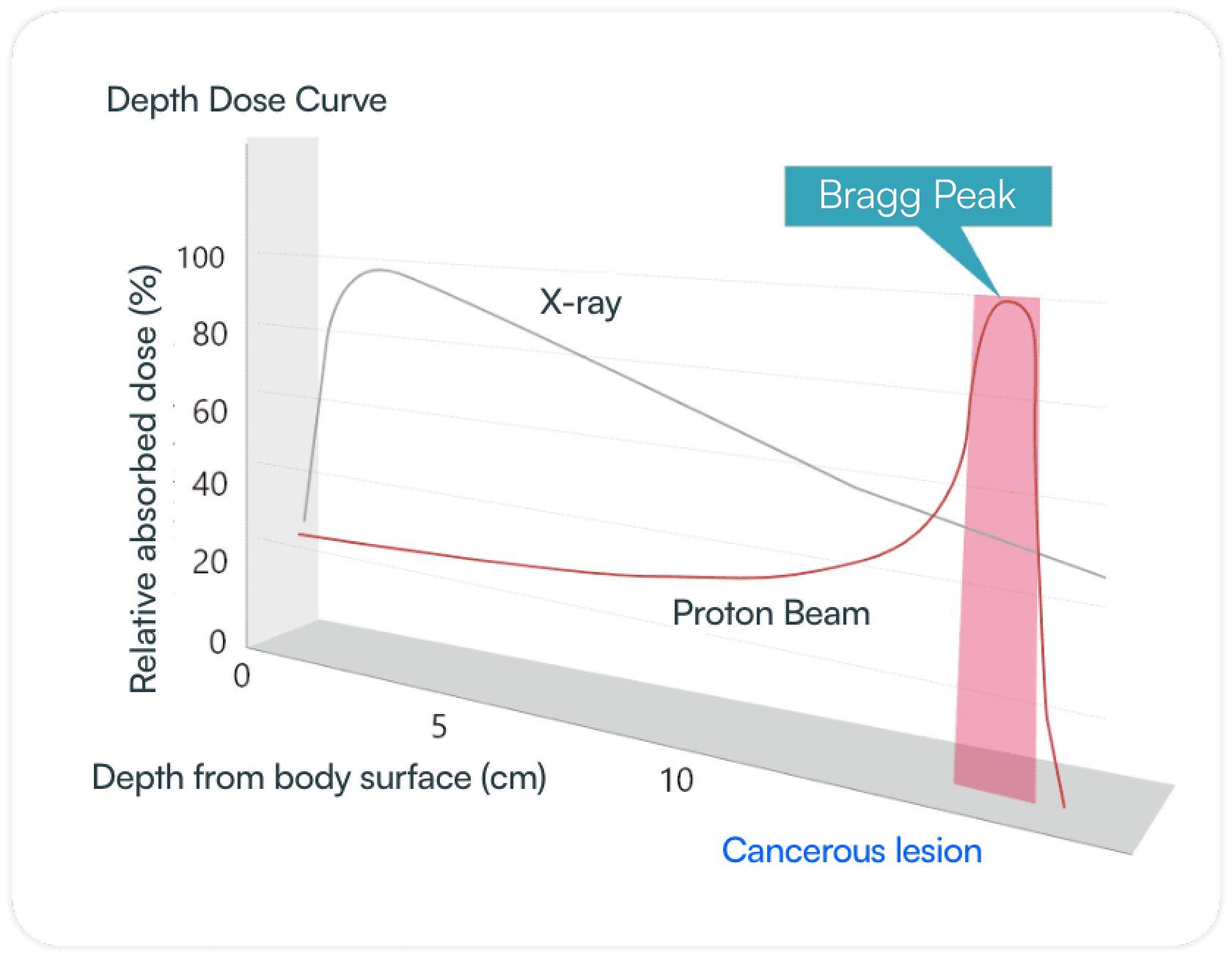
Bragg peak
When irradiated, protons have the characteristic of forming an energy peak just before stopping at a certain depth in the body and then stopping.
The proton beam stops exactly at the depth of the tumor. Irradiation of surrounding normal tissue is minimized.
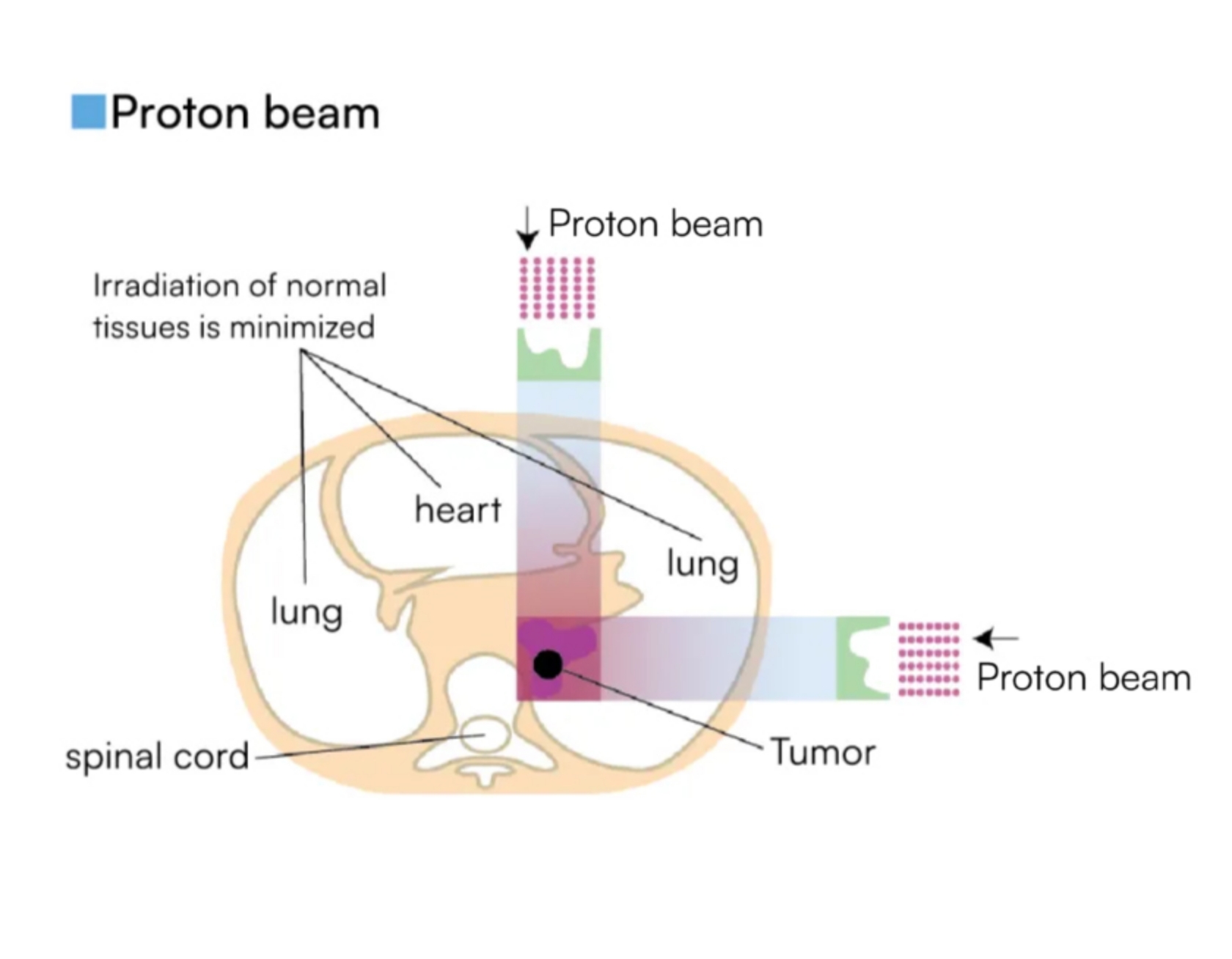
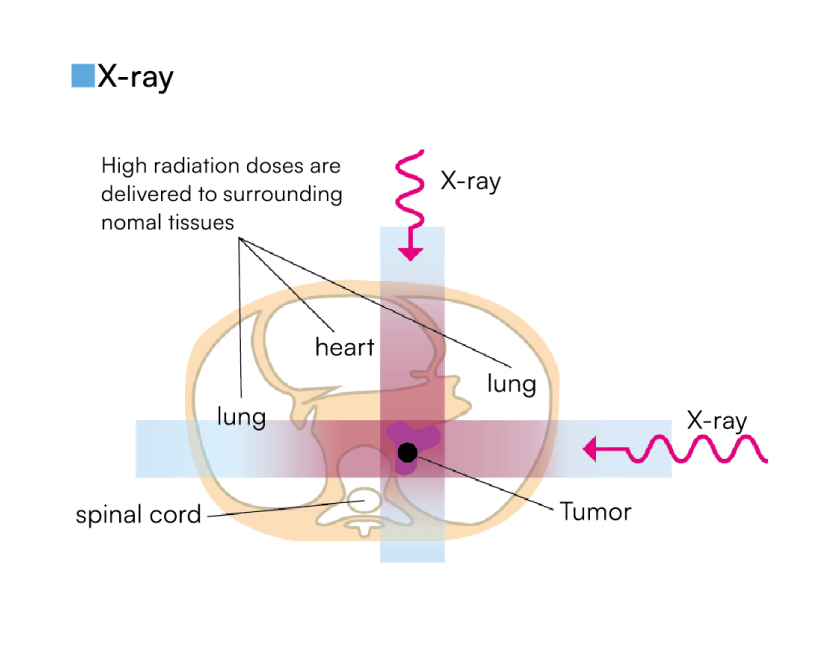
Dark coloured areas show higher radiation levels
